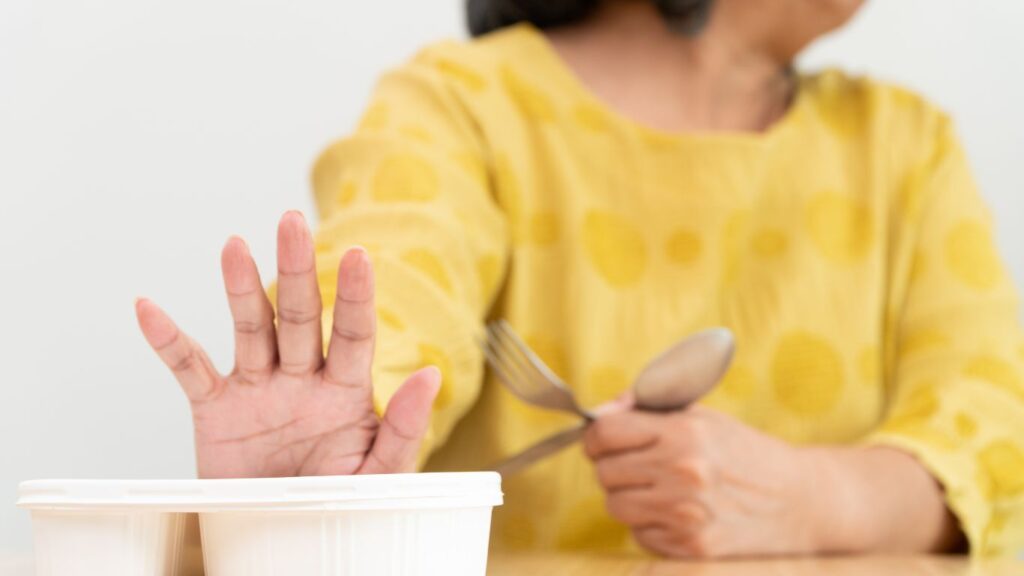
What Causes Loss of Appetite in Older Adults?
It’s not uncommon for older adults to experience a loss of appetite. This age-related change, known as the “anorexia of aging,” goes beyond simply skipping
Downey Community Health Center (DCHC) is a 198 bed skilled nursing facility in Downey, CA for those who need short-term recuperation and rehabilitation or skilled care.






*I can’t say enough about your staff and facility. You treated my father and got him ready to come home. Love you all!
— G.P.
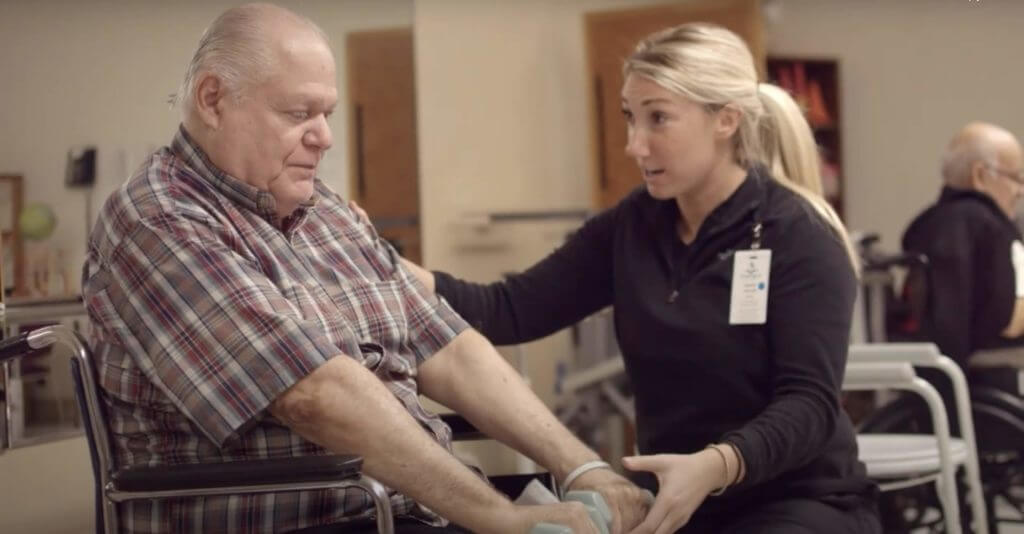
Downey Community Health Center (DCHC) is a 198 bed skilled nursing facility for those who need short-term recuperation and rehabilitation or skilled care. We have been serving Downey area residents since we opened our doors in 1980. With Medicare and private plans available, we offer several options to meet the needs of our residents.
Downey Community Health Center offers a range of therapeutic and rehabilitative programs that are meant to help our residents quality of life. An attending physician and other medical practitioners will assess the resident and develop a treatment plan to help the resident achieve functional gains while also increasing their independence. At DCHC, we believe that our residents should continue to live full and enriching lives.
Downey Community Health Center offers a wide variety of services
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

It’s not uncommon for older adults to experience a loss of appetite. This age-related change, known as the “anorexia of aging,” goes beyond simply skipping

Shaky hands or sudden muscle spasms in seniors might be more than just aging. They can be signs of something as simple as, and as

Driving is more than a way to get from one place to another. It represents freedom, independence, and staying connected to the world. For many

Moving into a nursing home is a big step. Understanding what a Downey nursing home daily life looks like can make the transition easier for

Finding the best nursing home for your loved one can be challenging, especially when you don’t know where to start. You have to take different

Choosing the right nursing home is a personal and emotional decision that directly affects your loved one’s comfort and quality of life. Key factors to