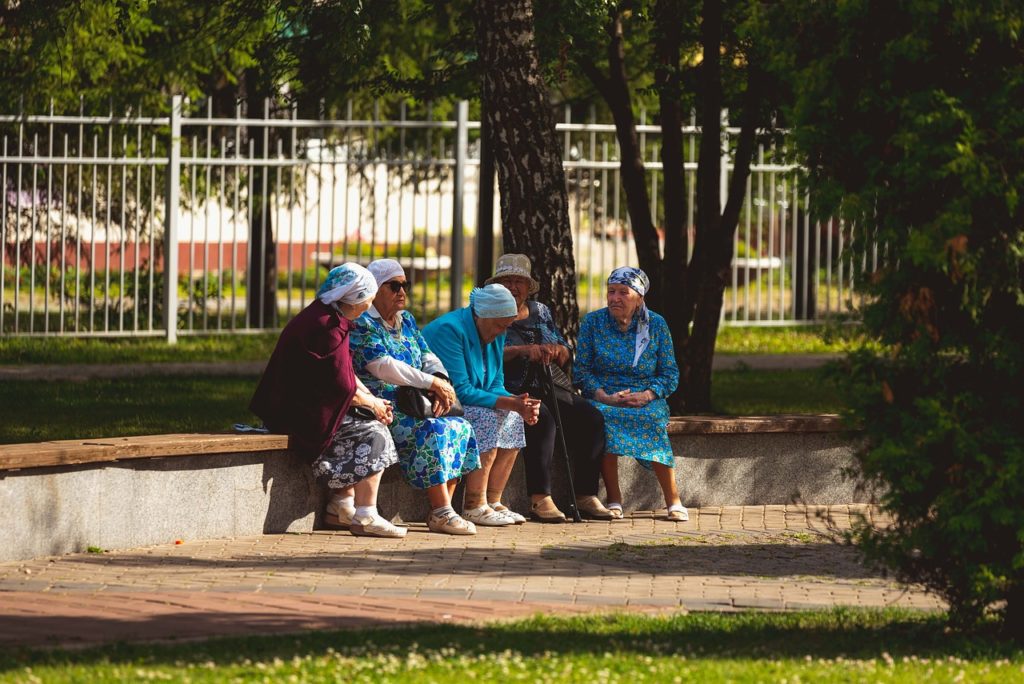
Community Care involves a holistic approach to meeting individuals’ health, social, and emotional needs within a community setting. This model emphasizes the collective responsibility of providing support and care, aiming to enhance the well-being of all members.
It seeks to offer personalized, accessible services that empower individuals, fostering independence and enabling them to remain integrated within their communities.
Community care is essential. It’s a lot more than self-care and it not only addresses the immediate health and social needs of individuals but also strengthens community bonds, creating a supportive network that contributes to overall societal health.
Since it focuses on preventive care and early intervention, Community Care reduces the strain on healthcare systems and promotes a more sustainable approach to welfare. Furthermore, it ensures that care is culturally sensitive and tailored to meet the diverse needs of community members, enhancing equity and inclusion.
Historical Perspectives
Community care finds its roots in early societies’ informal networks, where family, friends, and neighbors support those in need. This approach was the primary means of social welfare before the advent of formal institutions.
Over time, as societies evolved and urbanized, the complexity of care needs grew, prompting the establishment of organized community care services. These shifts were driven by various social reform movements, particularly during the 19th and 20th centuries, aiming to improve living conditions, health outcomes, and access to education and support services.
The evolution of community care reflects broader societal changes, including advances in healthcare, people’s personal experiences, social policy reforms, and growing recognition of the rights of individuals to receive care within their communities, framing current practices that emphasize inclusivity, personalization, and integration of services.
Principles Underlying Community Care
Community care is built upon a foundation of core principles designed to guide its practice and implementation. These principles ensure that care is delivered in a way that is equitable, effective, and respectful of the needs of the community it serves.
Accessibility
Accessibility is crucial in community care, ensuring that services and support are readily available to those who need them, regardless of their geographical, socioeconomic, or physical circumstances.
This principle advocates for the removal of barriers that restrict access to care, including financial, cultural, and logistical obstacles, making it possible for every member of the community to obtain the help they require without undue hardship.
Holistic Approach
A holistic approach to practice community care emphasizes the treatment of the whole person, rather than focusing solely on the symptoms or issues they are experiencing.
This perspective considers the physical, emotional, social, and spiritual dimensions of an individual’s well-being and seeks to address the broad range of factors that can affect health and quality of life. By adopting a holistic approach, community care providers can offer more comprehensive and effective support to those in need.
Empowerment
Empowerment is a critical principle that empowers individuals and communities to take control of their health and well-being.
It involves equipping people with the knowledge, skills, and resources they need to make informed decisions about their care, encouraging active participation in their own health journeys. Empowerment fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, leading to more engaged and proactive approaches to health and wellness.
Inclusivity
Research shows that inclusivity ensures that community care services are designed and implemented in a way that is welcoming and accessible to everyone, regardless of their background, identity, or circumstance.
This principle is about celebrating diversity and working to ensure that all members of the community feel valued, respected, and supported.
Inclusive community care recognizes the unique needs and strengths of different groups and individuals, striving to provide care that is respectful, culturally sensitive, and tailored to the diverse community it serves.
Models of Community Care
In the evolving landscape of health care, several models stand out for their effectiveness in improving health outcomes and fostering supportive environments for diverse populations. These models include:
Healthcare Systems Integration
This model emphasizes the seamless integration of services across the healthcare continuum, from primary care to specialized medical services.
Healthcare systems integration aims to create a coordinated network where patients’ information flows smoothly between different healthcare providers, ensuring that individuals receive timely and appropriate interventions.
This approach not only improves patient outcomes but also enhances the efficiency of healthcare delivery and reduces unnecessary duplication of services.
Community-Based Organizations
Community-based organizations (CBOs) play a crucial role in the community care model by providing services focused on health promotion, disease prevention, and social support.
These organizations are deeply rooted in the communities they serve, allowing them to tailor their services to meet the unique needs of their constituents. Each of them will provide support for a person’s everyday life, allowing them to prevent social isolation, put them on a path to community healing, and as a whole, be a stepping stone in their path for a better life.
CBOs work in partnership with local healthcare providers and public health agencies to address the social determinants of health, offering a holistic approach to well-being that extends beyond traditional medical care.
Peer Support Networks
Peer support networks are comprised of individuals who share similar health experiences or challenges. These networks offer emotional, social, and practical support to their members, helping them to manage their conditions and improve their quality of life.
Peer support can take various forms, including face-to-face meetings, online communities, a support group, or one-on-one mentoring.
This model leverages the power of shared experiences to foster a sense of belonging, encourage healthy behaviors, and provide a valuable complement to formal healthcare services.
Components of Community Care
Community Care examples must rely on a holistic approach to healthcare, aiming to support individuals’ health and well-being within the context of their communities.
This approach can recognize the different facets of health, incorporating various components to address the comprehensive needs of community members, for example, understanding that people with similar experiences will provide a lot of value to the group’s efforts as well as to the organization as a whole.
Preventive Healthcare Services
Preventive healthcare services focus on preventing illness before it occurs. This encompasses a wide range of activities, such as vaccinations, regular health screenings, and education on healthy lifestyle choices.
When they prioritize prevention, communities can reduce the occurrence of chronic diseases, decrease healthcare costs, and benefit the overall quality of life for individuals.
Mental Health Support
Mental health support is another crucial aspect of Community Care. This includes providing access to mental health professionals, support groups, and educational resources aimed at raising awareness and reducing stigma around mental health issues.
The objective is to create an environment where individuals feel supported in their mental health journeys and can easily access the help they need when they need it.
Social Services
Social services play a vital role in addressing the socioeconomic factors that affect health and well-being. These services may include but are not limited to, assistance with housing, employment, education, and food security.
By addressing these foundational needs, social services help in creating a stable environment that supports healthy living and resilience against illness.
Through the integration of preventive healthcare, mental health support, and social services, Community Care aims to deliver a comprehensive approach to health that is proactive, responsive, and tailored to the diverse needs of community members.
Benefits of Community Care
Community care, often a linchpin in the fabric of health services, offers a broad spectrum of advantages that extend well beyond the mere provision of medical interventions.
The impacts of such an approach are multifaceted, emphasizing not only the importance of treating illness but also the critical need for prevention, rehabilitation, and the ongoing support of individuals within their own communities.
A. Improved Health Outcomes
Community care plays a pivotal role in improving health outcomes for individuals. If they are offered healthcare services within familiar, accessible environments, patients are more likely to seek timely medical attention, adhere to treatment plans, and engage in preventative care measures.
This localized approach to healthcare ensures that interventions are culturally sensitive and tailored to meet the unique needs of the community, improving the overall effectiveness of care.
Enhanced Well-being
The philosophy of community care extends beyond physical health, greatly contributing to the enhanced well-being of individuals. It fosters a sense of belonging and support by connecting people with local resources, social networks, and community groups.
This holistic approach addresses the social determinants of health, such as isolation and socioeconomic status, which are crucial for mental and emotional well-being.
Cost-Effectiveness
From an economic perspective, community care models are cost-effective. They reduce the reliance on hospital-based services, long-term care facilities, and other high-cost healthcare settings by providing early intervention and ongoing support in the community.
This not only leads to better health outcomes and reduces the financial burden on the healthcare system but also alleviates the economic strain on patients and their families by minimizing travel expenses, lost work, and other costs associated with receiving care in distant or specialized facilities.
Conclusion: Embracing Community Care for a Better Future
Throughout this discussion, we’ve explored the essential principles and practices that underpin the effective implementation of community care. We’ve seen how community-based approaches can not only enhance the quality of life for individuals but also strengthen the fabric of communities themselves.
By prioritizing local involvement, tailoring services to meet specific needs, and fostering a culture of empathy and support, community care initiatives can address a wide range of health and social needs in a more personalized and efficient manner.
As we look to the future, it is clear that the adoption of community care models has the potential to transform our approach to health and well-being significantly. To this end, we must all take active roles in advocating for and participating in community care strategies within our own environments.
Whether it’s through supporting local health initiatives, volunteering time and resources, or simply spreading awareness about the benefits of community care, every action contributes to building a stronger, healthier, and more connected society.
Together, we can work towards a future where community care is not just a concept, but a fundamental part of how we look after each other.